Steady-State Thermal Analysis
What Is Steady-State Thermal Analysis?
Steady-state thermal analysis is evaluating the thermal equilibrium of a system in which the temperature remains constant over time. In other words, steady-state thermal analysis involves assessing the equilibrium state of a system subject to constant heat loads and environmental conditions. The simplest form of steady-state analysis is linear steady-state analysis in which input parameters, such as material properties, are prescribed independent variables.
Real systems exhibit non-linear steady-state behavior. Non-linear steady-state analysis is where input parameters are interdependent. In such cases, a solver must iterate to find a steady-state solution to the governing equations that satisfy the input parameters. Examples of systems with non-linear characteristics include those with temperature-dependent thermal conductivity, radiation, or natural convection.
Why Is Steady-State Thermal Analysis Important?
For many simulations, steady-state thermal analysis can be used to design and evaluate systems, even throughout the final stages of the design process. For example, steady-state thermal analysis can be used when simulating a server’s thermal state, which typically remains constant over time. Steady-state thermal analysis is also beneficial when used to guide early design and prototyping efforts with quick feedback for simple models. It facilitates design decisions for typical operating conditions and acts as a baseline for transient analysis of controls and failure analysis.
3 Examples of Steady-State Thermal Analysis
1. Prototyping and Early Design
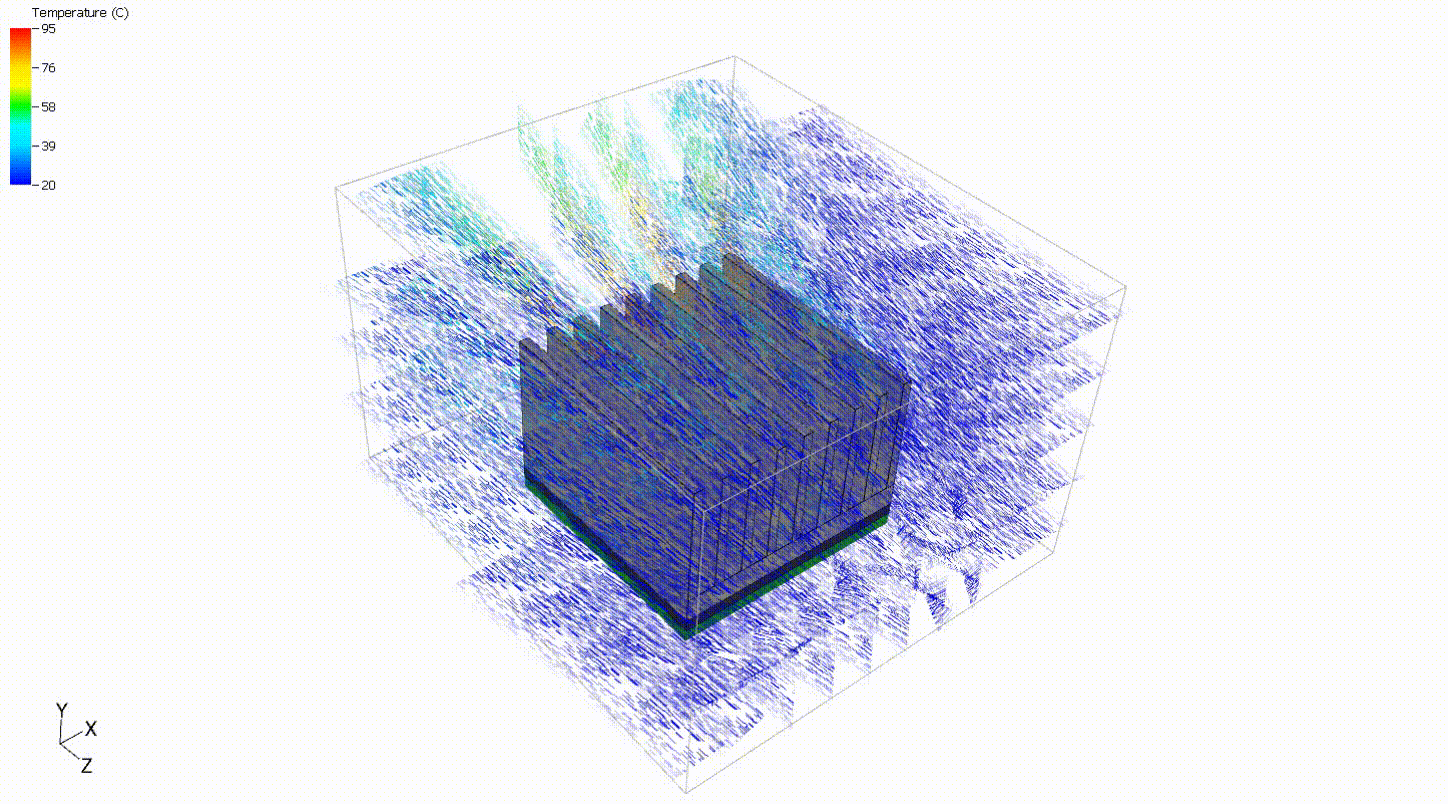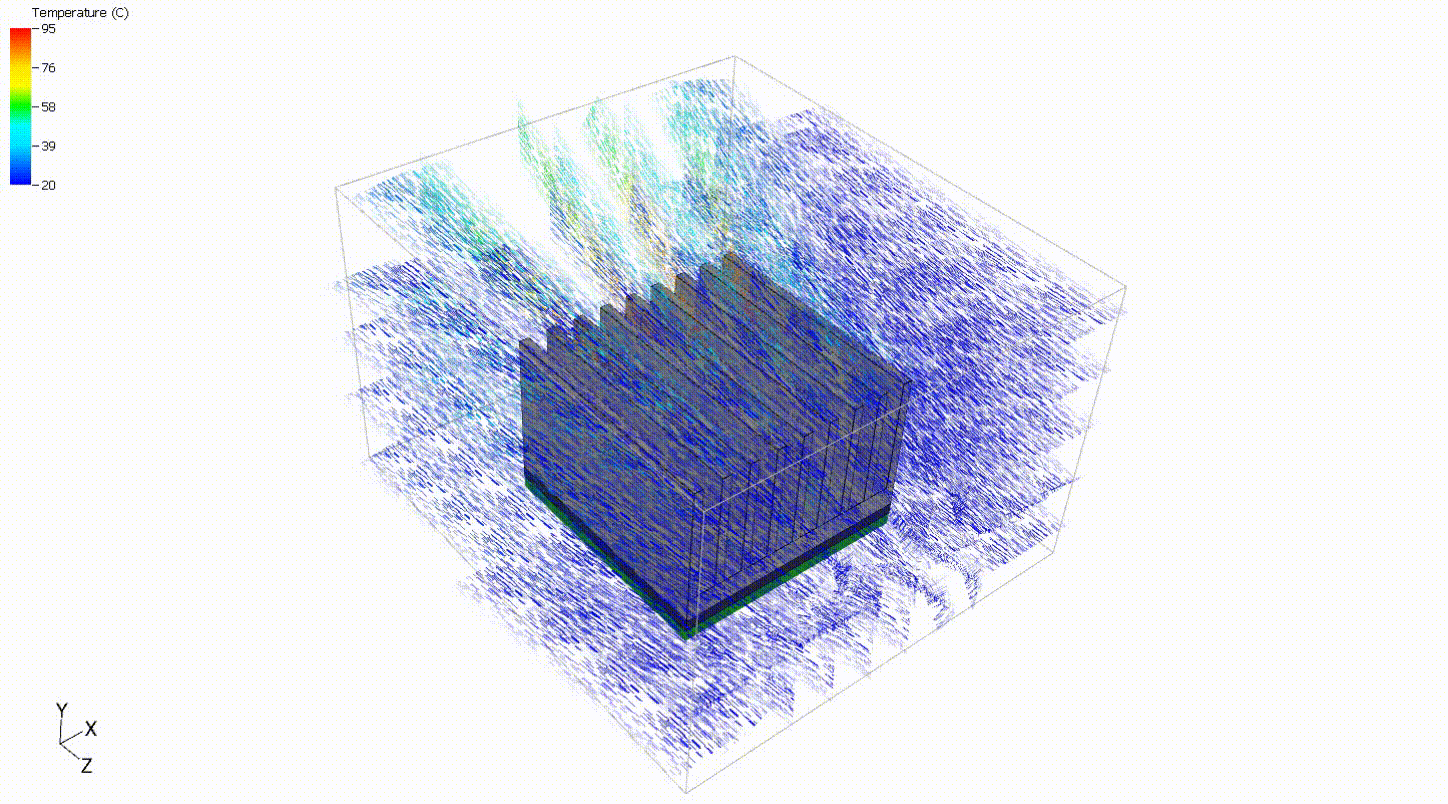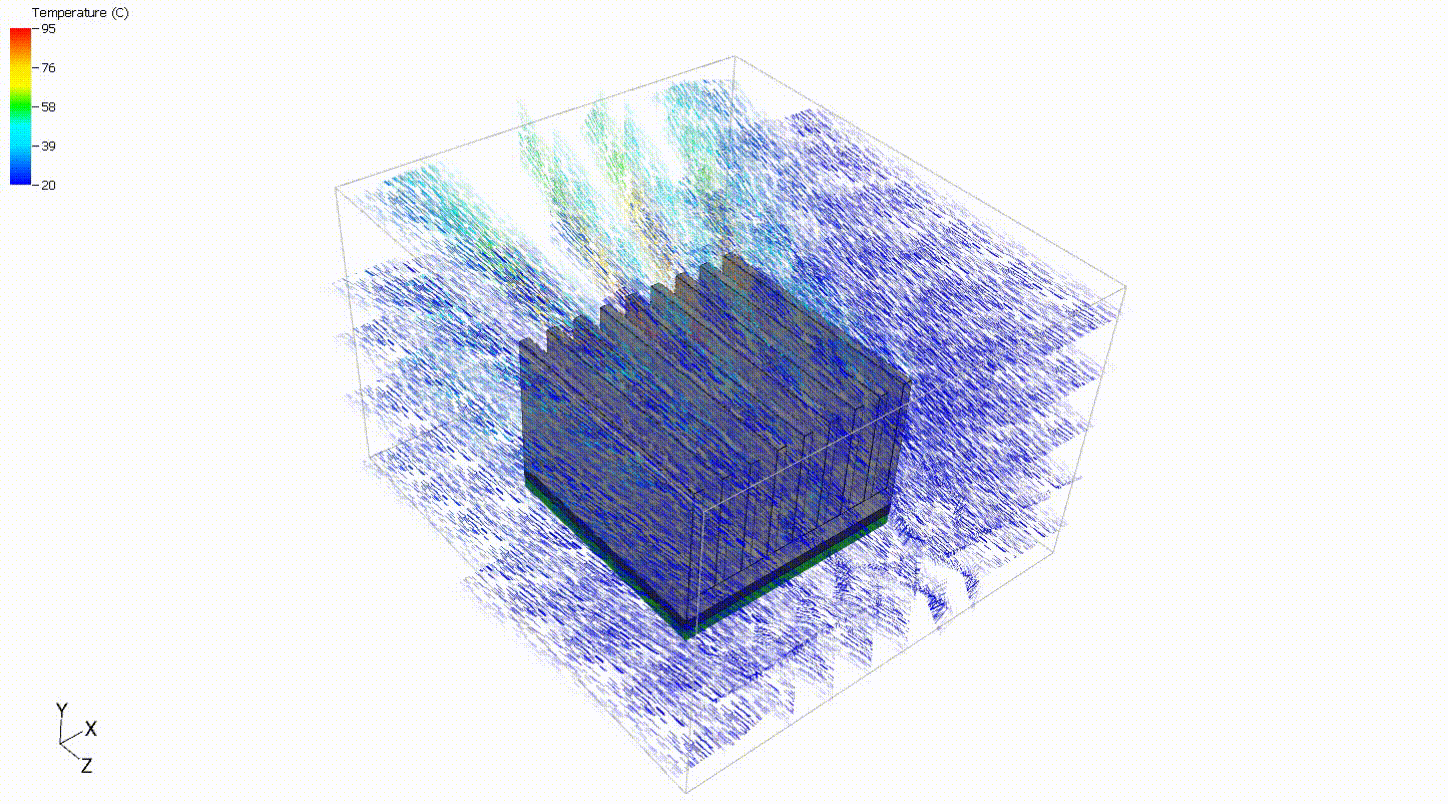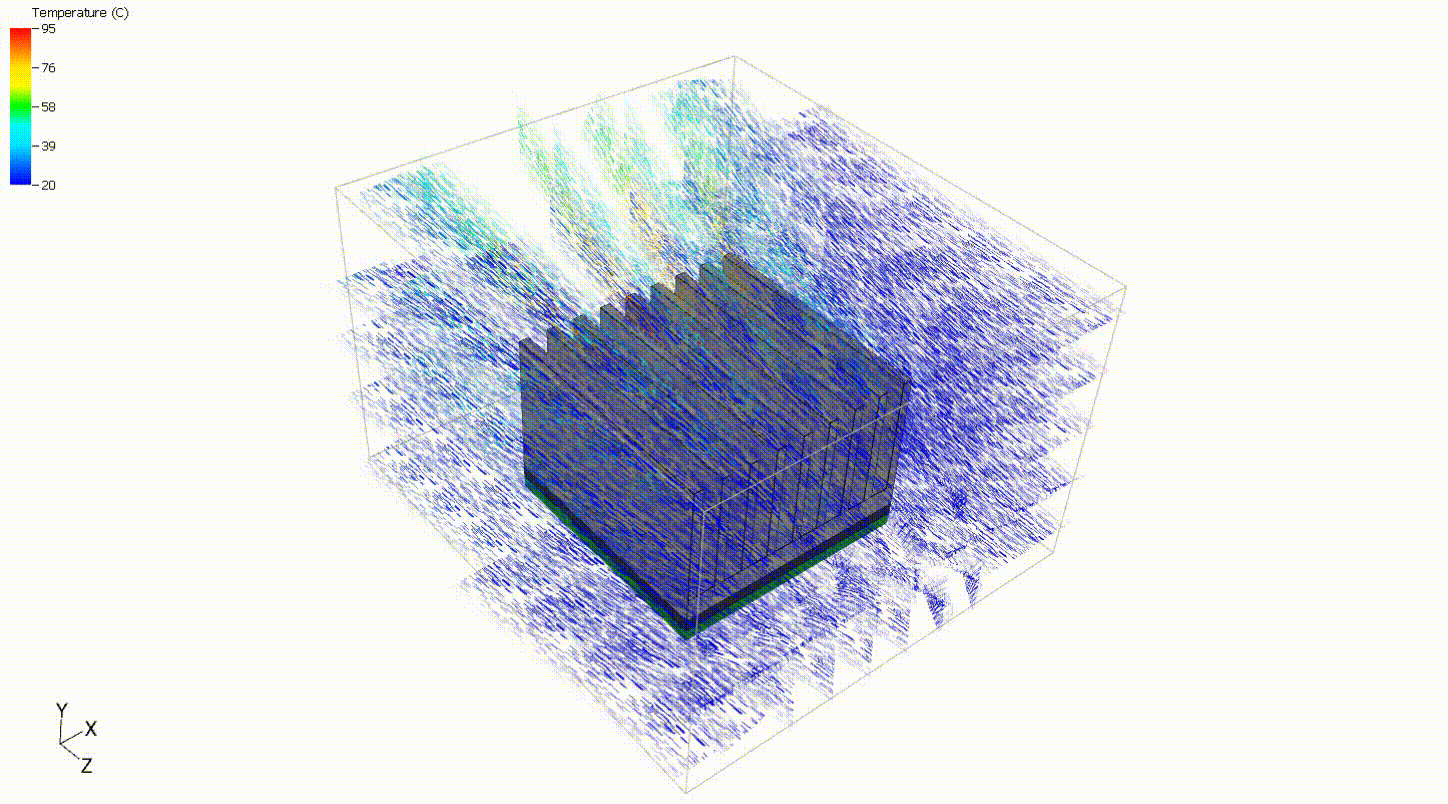
A simple model of a heat sink can be used to evaluate off-the-shelf components to decide on a heat sink that best meets the design criteria. In such a scenario, the heat sink can be placed in a full system model or flow data can be extracted from simulation or testing results to give approximate boundary conditions. For this situation, a simple steady-state analysis with prescribed boundary conditions is sufficient to compare heat sinks. The flow rate and component power are assumed to be constant. Although it is always good practice to verify design decisions with full system models and physical testing, a simple steady-state thermal analysis can provide a good starting point.
2. Evaluating Standard Operating Conditions
Another application of steady-state thermal analysis is evaluating system performance under typical operating conditions. This can be considered a pro forma analysis, with operating conditions associated with the typical use case and normal operation. From this, design decisions can be made and system performance predicted.
3. Precursor to Transient Analysis
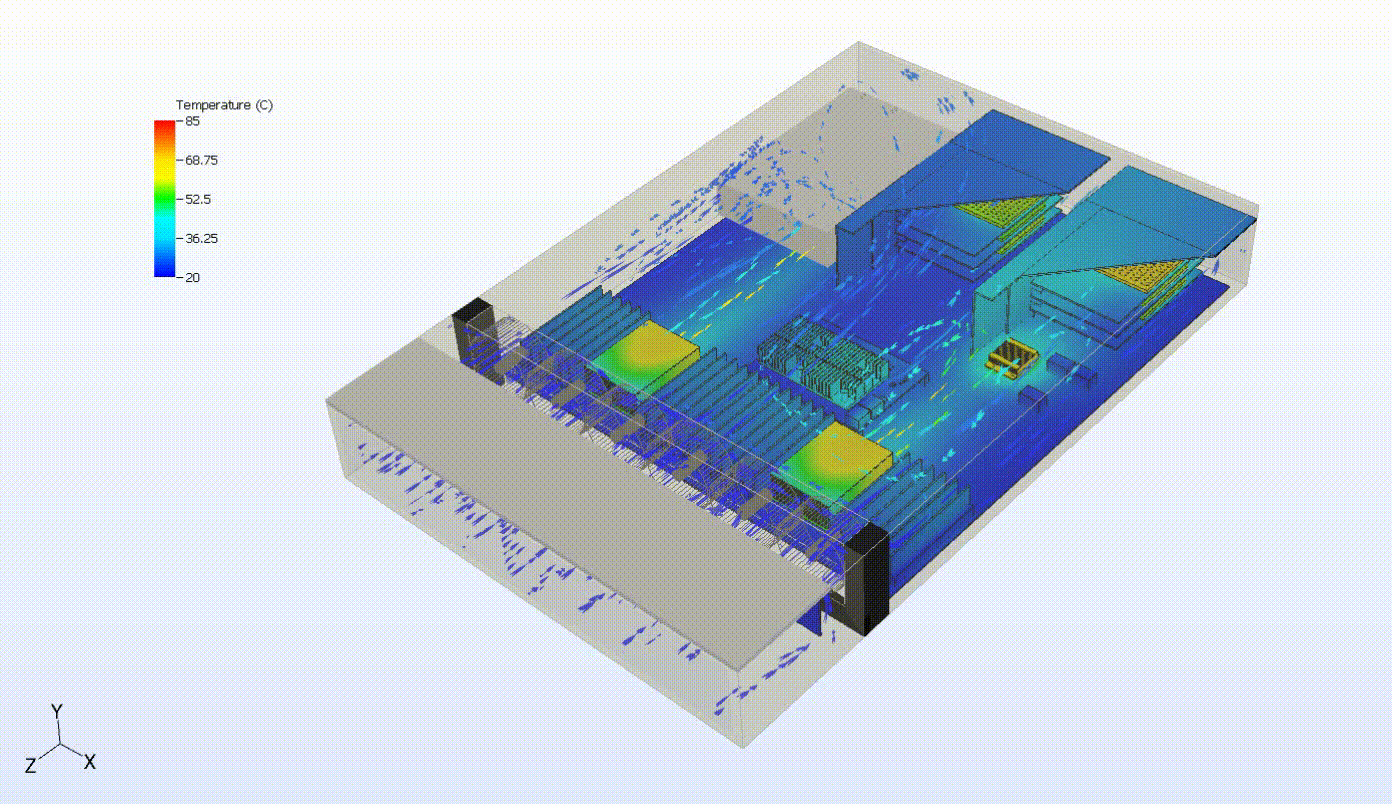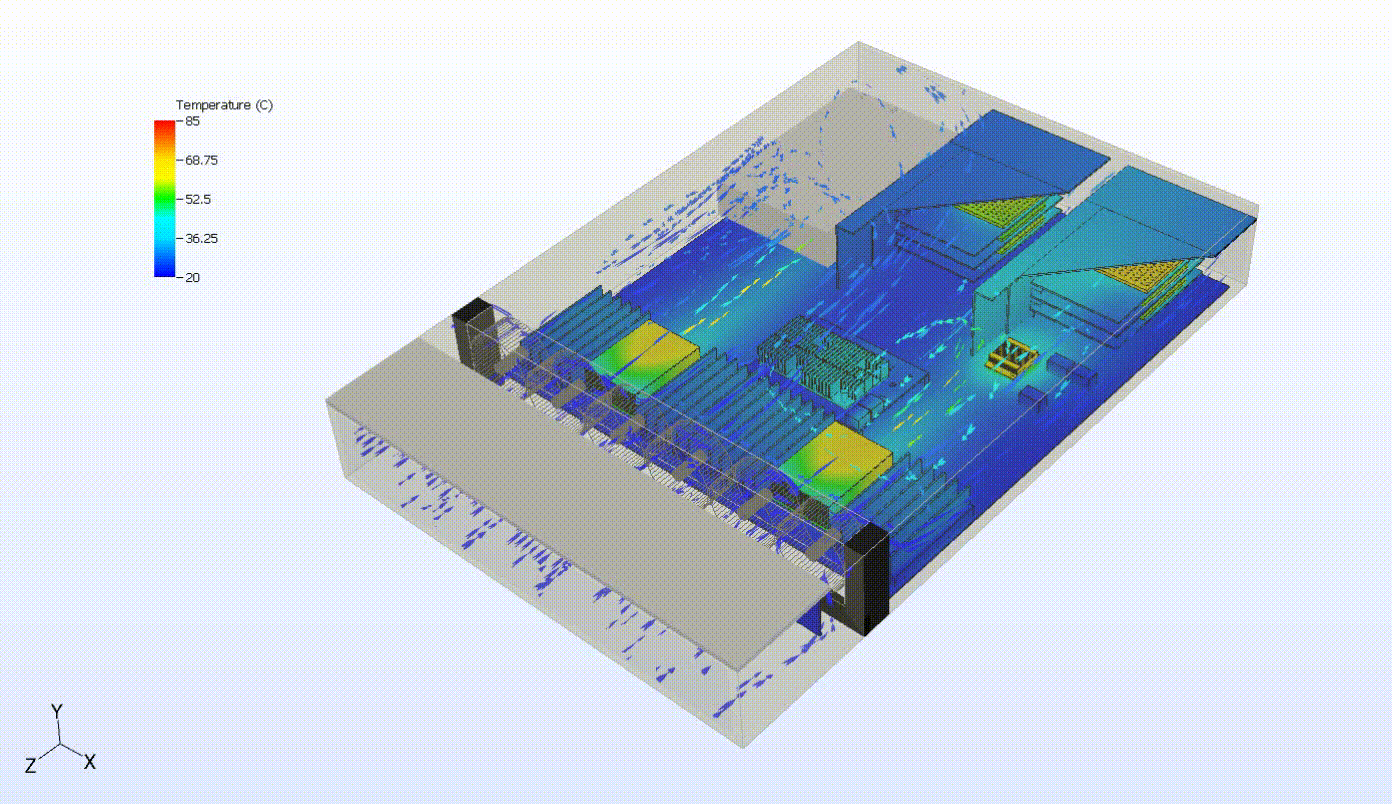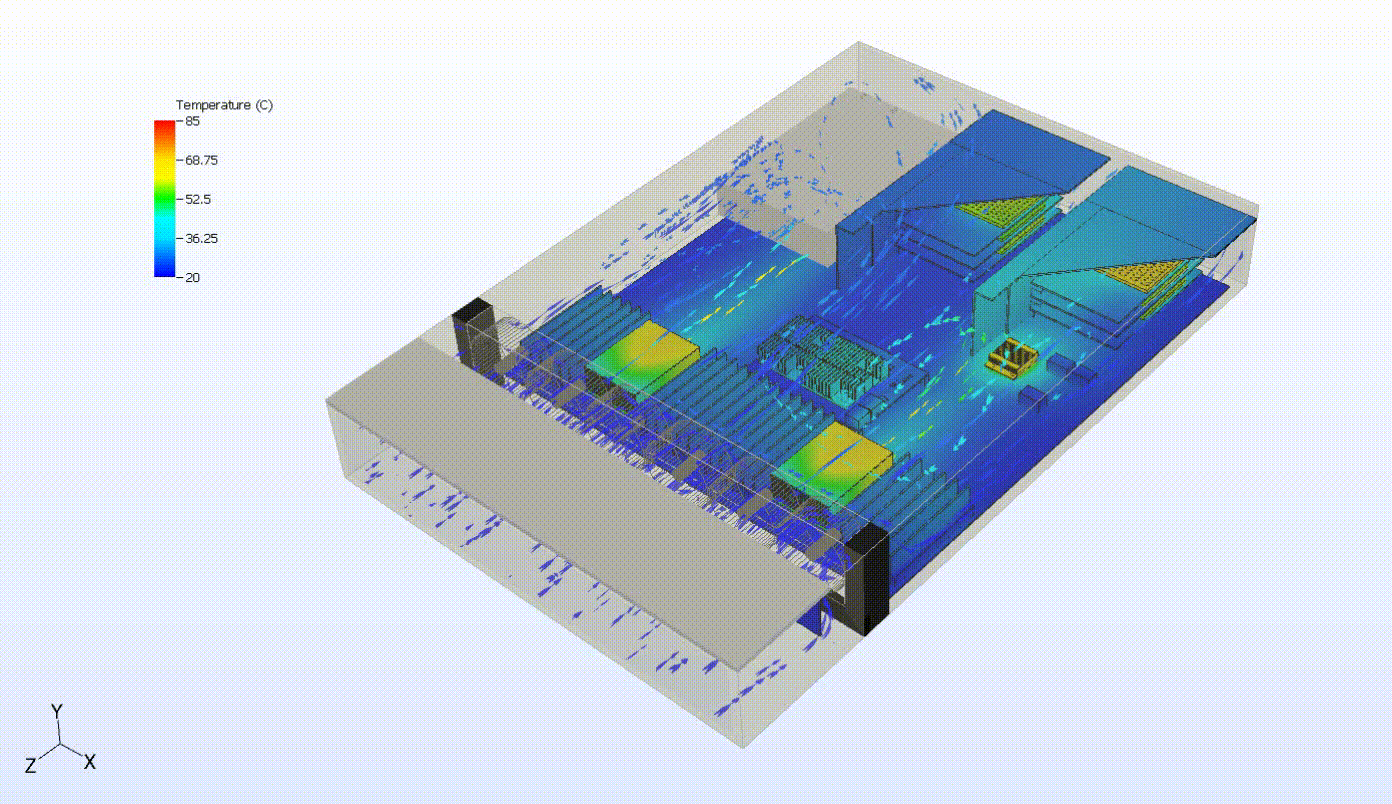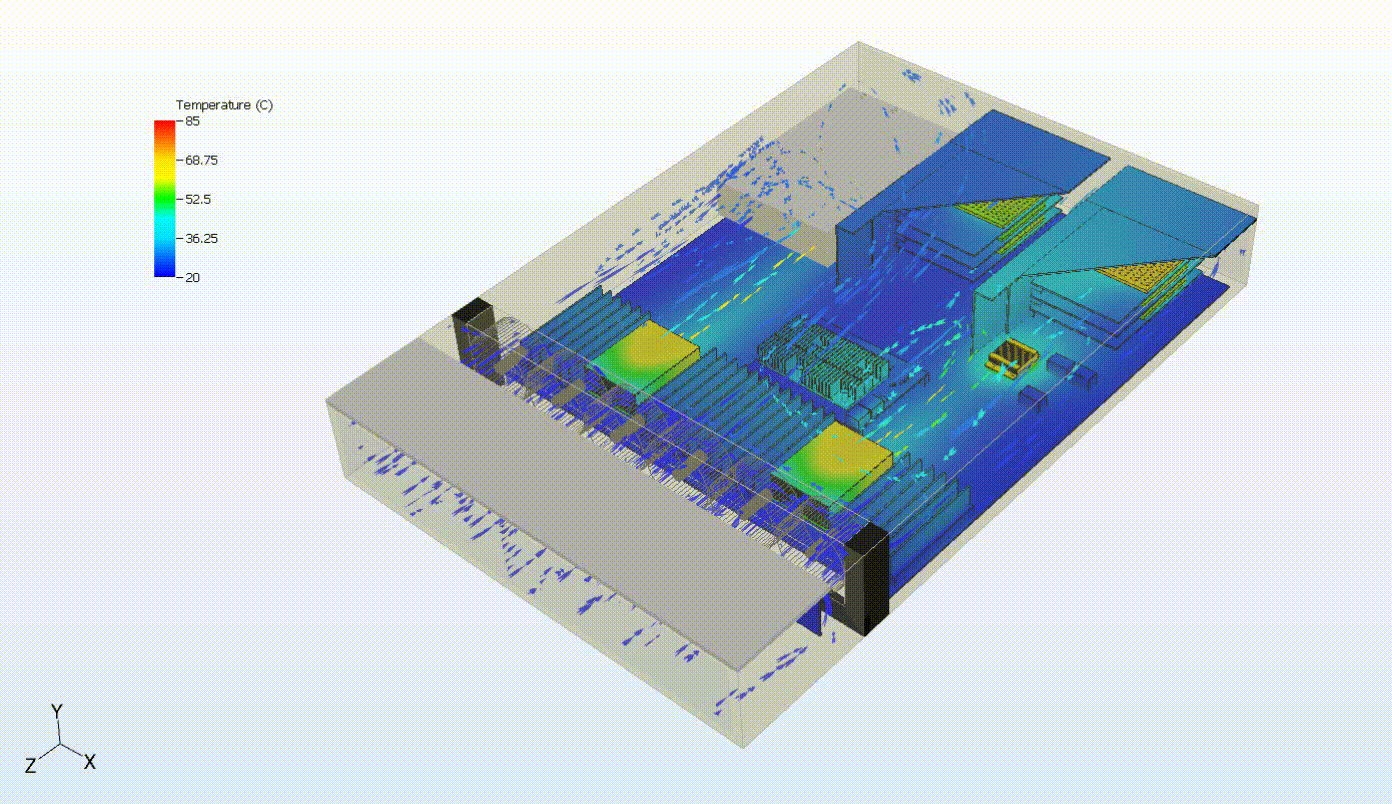
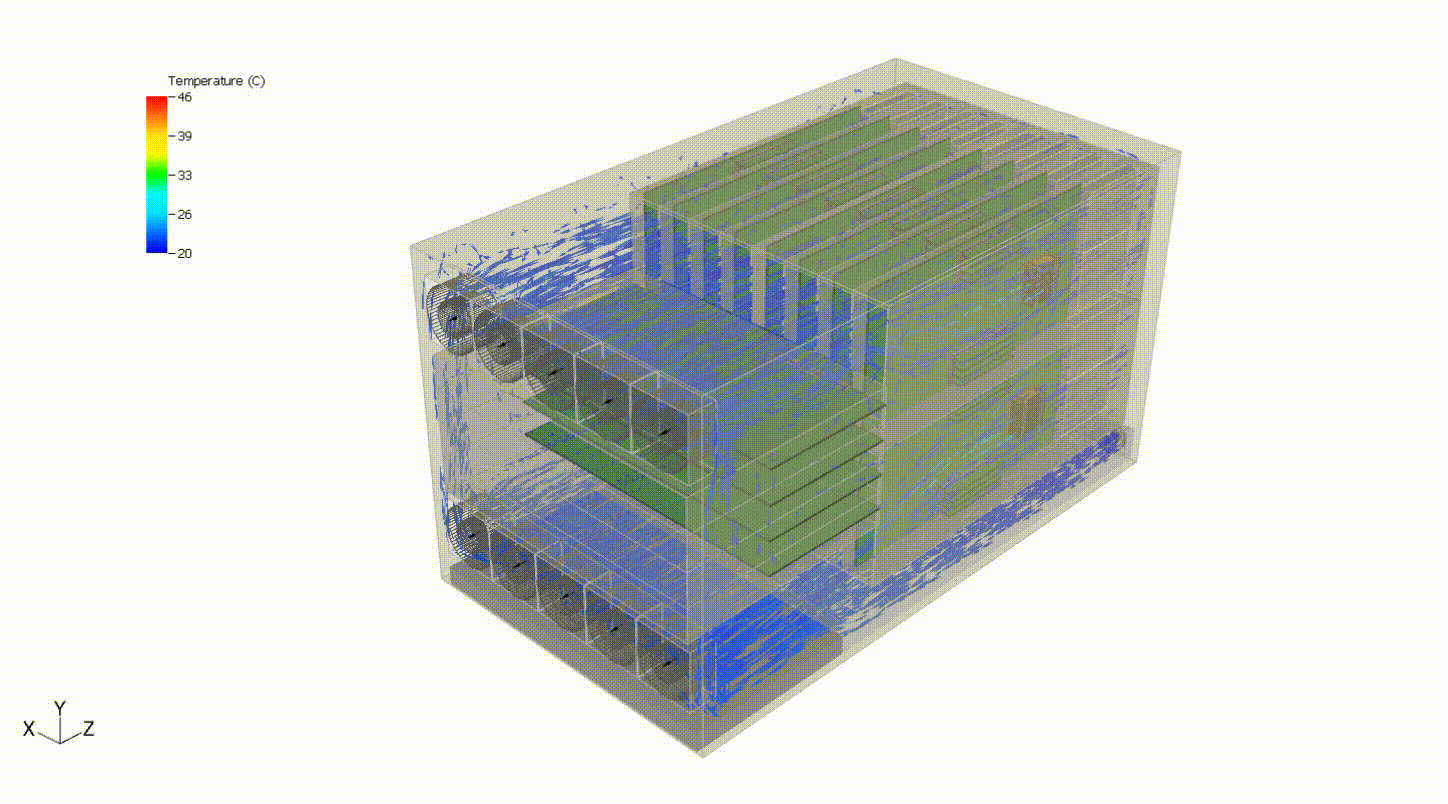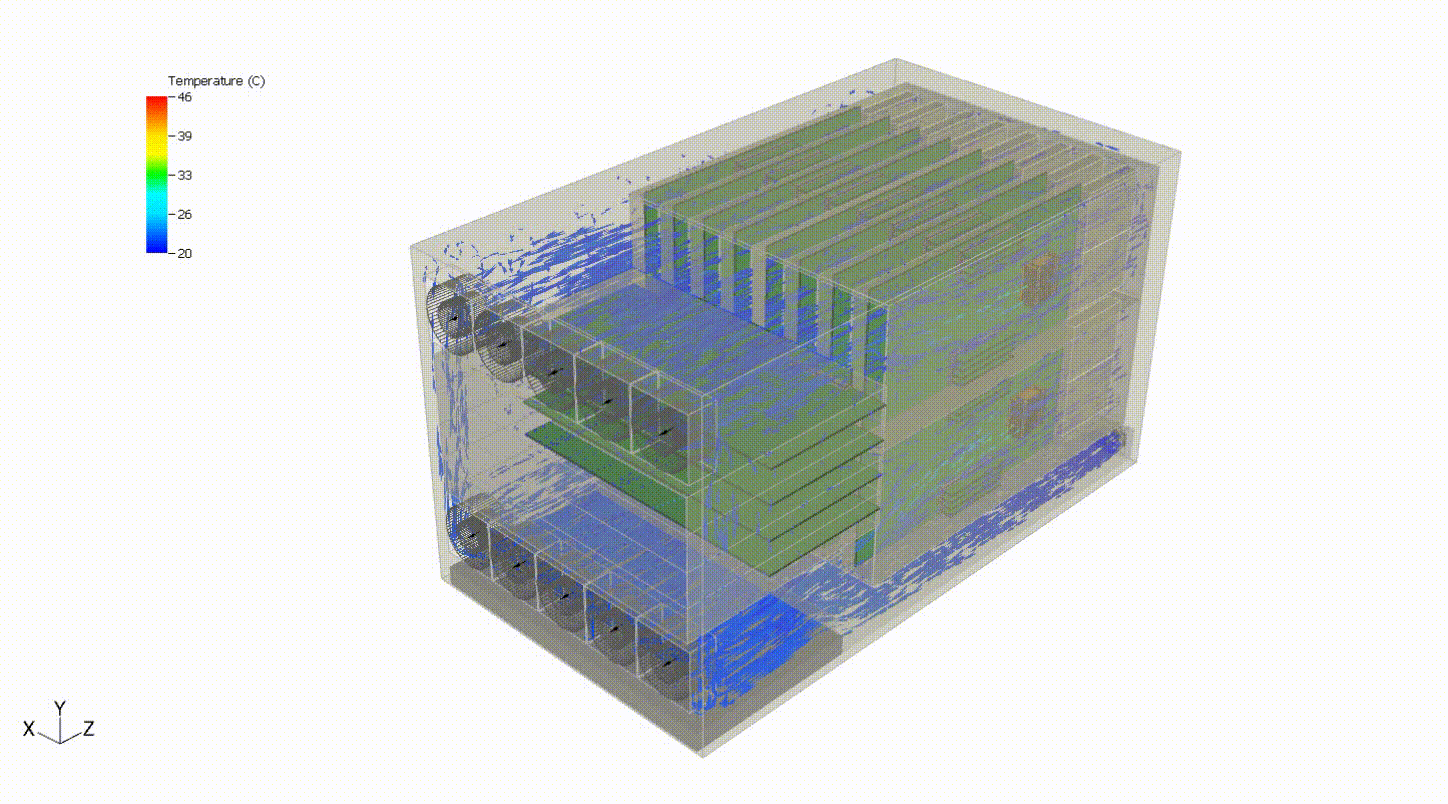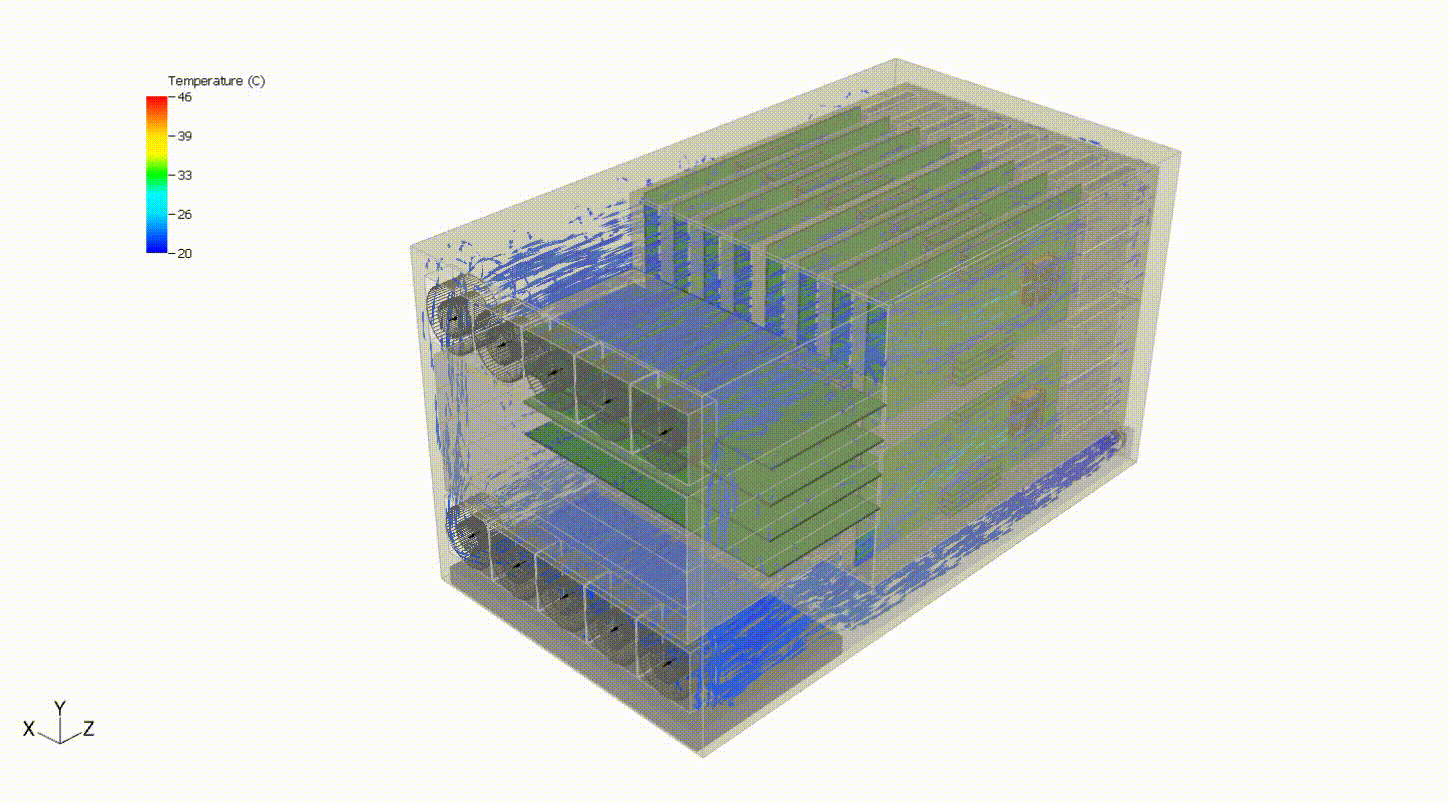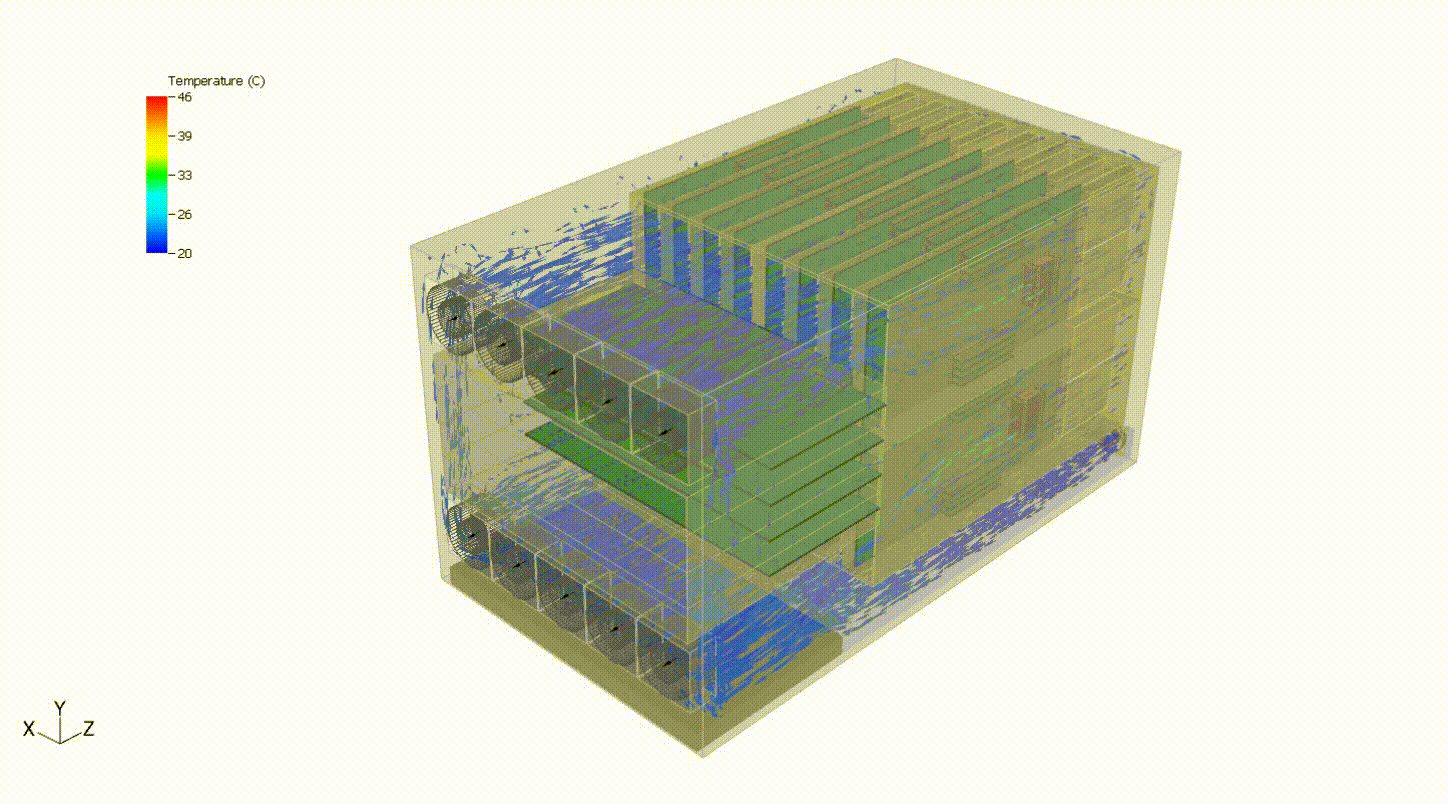
Steady-state thermal analysis can also be used as a precursor to transient thermal analysis. For example, someone interested in cooling failure analysis might want to see the effects of a failure in some portion of the cooling capacity of the system. In the system below, we can evaluate the system response to a failure of the top fan tray. We first need to simulate the steady-state behavior of the system at normal operating conditions. Then, we turn off the fan tray and run a transient simulation to evaluate the thermal response of the system following the failure. This may also involve various control systems, including fan controllers and power throttling.
Steady-State Thermal Analysis and Thermal Simulation
Steady-state analysis is the fundamental tool used to evaluate the thermal behavior of electronics systems. It can be used to guide design decisions from concept to final design. Cadence Celsius EC Solver is a leading electronics thermal simulation tool with the capability to evaluate electronics systems using both steady-state and transient thermal analysis.